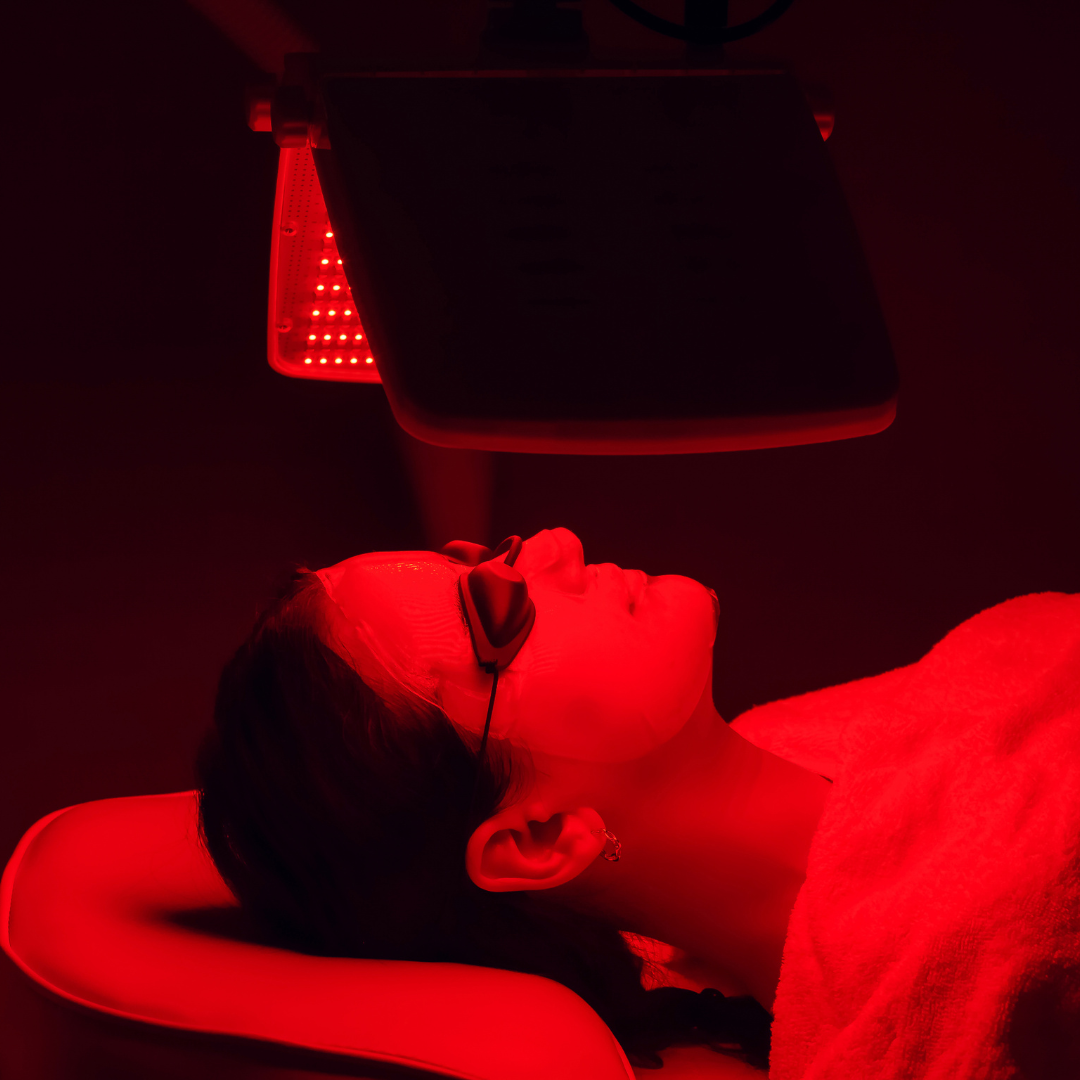
Treatment using Red Light Therapy Device is a relatively new option that is rapidly gaining popularity. When you first hear about red light therapy, you probably have a lot of questions. With so many scientific terms and hard-to-pronounce words like "photobiomodulation", you're probably scratching your head.
Don't worry. We've got you covered in this deep dive into red light therapy. We'll cover exactly what red light therapy is, the science behind how it works, and how it affects the body before and after treatment.


During red light therapy, what is happening in our body? How does red light therapy benefit?
Effective red light therapy improves cellular metabolism and reduces inflammation through a photochemical response. In this process, red and infrared light increases cellular production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). You may remember from biology class, "The mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell!"
When cells are stressed, they perform poorly because nitric oxide molecules bind to ATP, preventing it from functioning properly. Red light therapy penetrates the mitochondria, detaching nitric oxide from ATP and allowing it to bind to oxygen instead. This rejuvenates mitochondrial function and ATP efficiency, and the nitric oxide molecules released from the cells act as vasodilators, increasing blood flow to the treatment site and surrounding areas.
This process is similar to photosynthesis in plants, where light triggers chemical reactions. In cells, these photochemical reactions help them to work at full capacity, increasing energy levels. The resulting increased blood flow reduces inflammation and pain, underlining the effectiveness of the red light therapy.